
Temperature in C + 273 = Temperature in Kelvin. Temperature in F + 460 = Temperature in Rankine. = 1.986 cal/gmole-K.Ībsolute temperatures ( Rankine or Kelvin) are used in the ideal gas law.

The bottom of the column of liquid, with 11 meters high and with a density due to gravity *height of liquid column.Įxercise: Determine the absolute and gauge pressure exerted at Of the column of liquid, with 1m height and with a density of 1200 Kg/m3. Is equal to 101.3 KPa absolute (760mm of mercury or 2116 lbf/ft 2).ĭetermine the pressure, both absolute and gauge, exerted at the bottom The average molecular weight of the mixture.Ītmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the atmosphere on the = 32*0.436 + 46*0.455+64 *0.109 = 41.858Įxercise: For a mixture equal weights of O 2 and SO 2,ĭetermine the mole fractions and weight fraction of each component and = (mol.wt of A * mole fraction of A) + (mol.wt ofī * mole fraction of B) + (mol.wt of C * mole fraction of C).Īvg. Weight of all the components in a mixture, if contains 20 lbs of O 2,įind the molecular weight(mol.wt.) of each gas.ĭetermine the number of moles of each gas. Total moles = moles A + moles B + moles C.ĭetermine the mole fraction, weight fraction and average molecular Mole fraction of A = ( Moles of A ) / ( Total moles ) Supposing a mixture has A, B, and C as its components. Of methanol is 0.91 multiplied by density of water = 1 g/cm 3. Weight Fraction, Mole Fraction, and Average Molecularįor example Specific gravity of methanol is given as 0.91. Ppm x molecular weight(g/mol) x 1000 ( mg*L/m 3*g)ġ.5 x 10 4 ppm x 28(g/mol) x 1000 ( mg*L/m 3*g)Įxercise: An exhaust gas containing 3.2 percent by volume SO 2 The exhaust from a 1981 Honda contains 1.5% by volume of carbon monoxide.Ĭompute the concentration of CO in milligrams/m 3 at 25☌ Molecular weight(g/mol) x 1000 ( mL/m 3*g)Įxercise: Carbon Monoxide concentration at 90☌ and 6 atm is Express this concentration in parts per millionĪT STP conditions (25☌ and 1 atm), one mole of gas occupies 24.5 L When corrected to a dry gas having a specified reference CO 2 content of 12 volume %.Introduction to Air Pollution - Workbook A I R PĪn SO 2 concentration is given as 830 mg/m 3Īt 25☌ and 1 atm. = measured concentration of a dry gas having a measured volume % CO 2Īs an example, a measured particulates concentration of 200 mg/m 3 in a dry gas that has a measured 8 volume % CO 2 is: = corrected concentration of a dry gas having a specified reference volume % CO 2
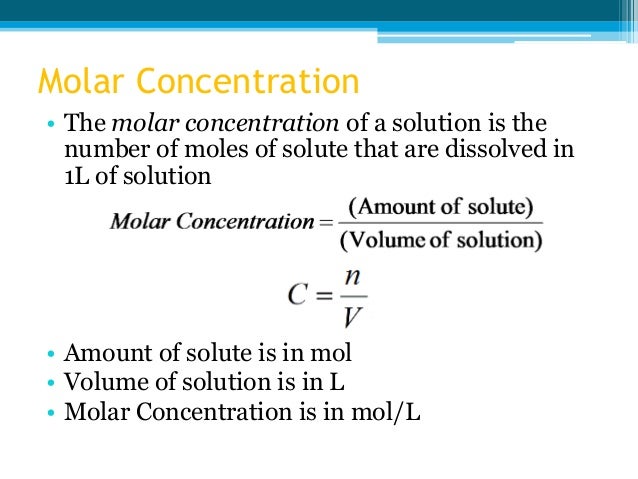
At an ambient sea level atmospheric pressure of 1 atm (101.325 kPa or 1.01325 bar), the general equation is: The conversion equations depend on the temperature at which the conversion is wanted (usually about 20 to 25 ☌).

Such regulations involve a number of different expressions of concentration. Regulations that define and limit the concentration of pollutants in the ambient air or in gaseous emissions to the ambient air are issued by various national and state (or provincial) environmental protection and occupational health and safety agencies. Air pollutant concentrations, as measured or as calculated by air pollution dispersion modeling, must often be converted or corrected to be expressed as required by the regulations issued by various governmental agencies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
